A Case Report of a Rare Aetiology of a Sigmoid Volvulus Involving a Congenital Omental Defect
Article information
Abstract
Sigmoid volvulus is a rare form of large bowel obstruction and makes up < 5% of all colonic obstruction. The commonest aetiologies include a lead point involving an intra or extra luminal mass such as a malignancy or a benign stricture or colonic dysmotility especially in the geriatric population. Rare aetiologies include a mesenteric defect, or as in this case report, a congenital omental defect acting as the lead point. This makes for an increasingly unusual case report, and we believe that this is the first such report in English language literature. The management remains the same, irrespective of the aetiology. Endoscopic bowel decompression in the acute phase is followed by definite surgical management with or without a primary surgical anastomosis.
Introduction
A colonic volvulus is a rare occurrence in the developed world, and usually makes up 2%–5% of all large bowel obstructions [1]. The majority of large bowel obstructions occur in the sigmoid colon, and in the elderly population with a history of chronic constipation and functional colonic dysmotility. This is in stark contrast to the Middle East where colonic volvulus is thought to account for 10%–80% of large bowel obstruction [1,2]. The low incidence is thought to be attributable to a change in the diet in the Middle East and population migration [2]. This case report is unique due to the young age of the patient as well the unusual aetiology involving a congenital omental defect with a band around the sigmoid colon.
Case Report
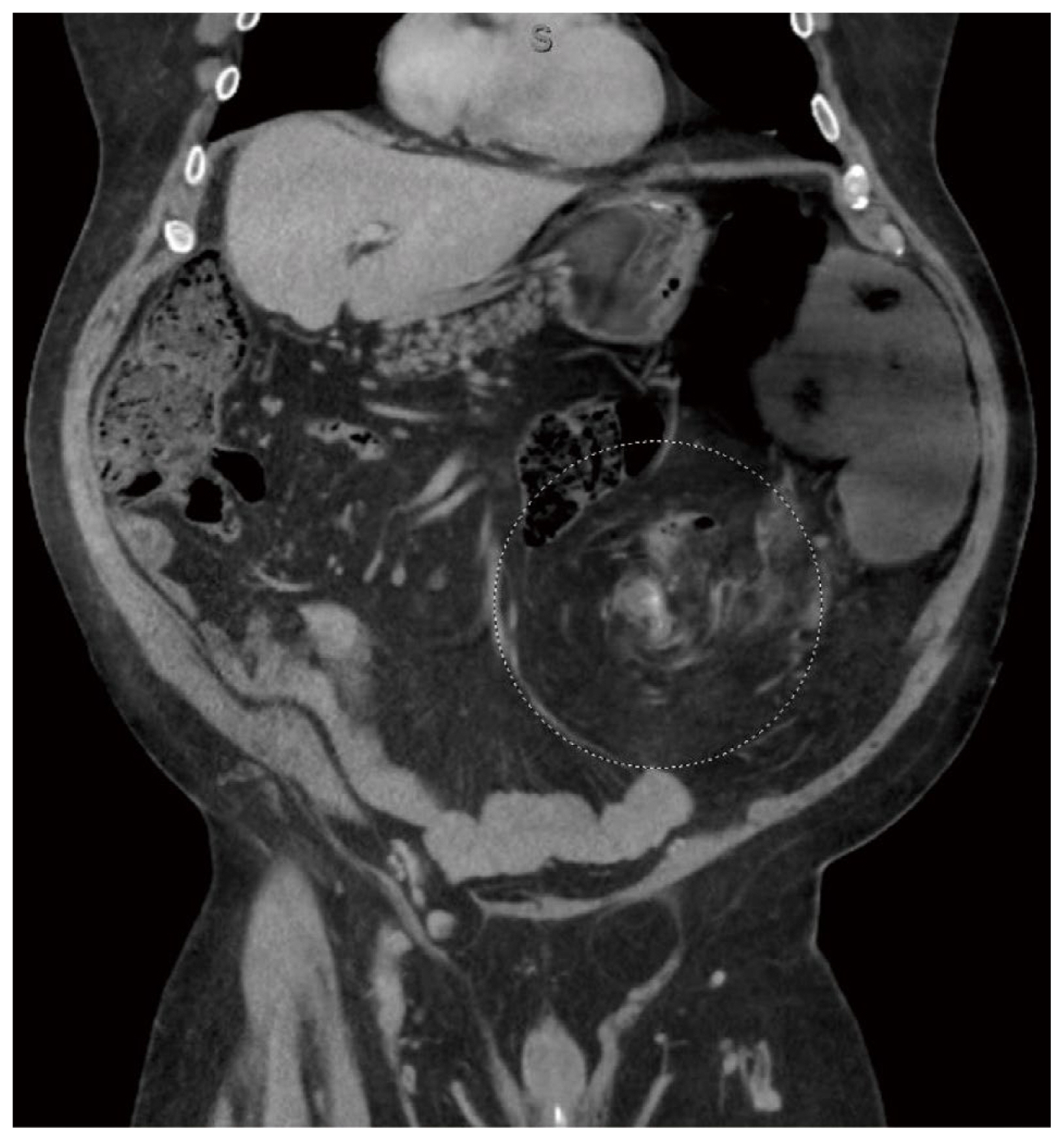
A 56-year-old man was referred from a rural clinic with a problem of bowel obstruction. He had abdominal pain and no history of abdominal surgery. There was nausea but no vomiting. He remained clinically stable, and his computerised tomography scan showed a sigmoid volvulus with no obvious signs of perforation or ischemia (Figures 1A and 1B). His abdominal examination revealed tympanic bowel with no signs of peritonitis. His biochemical and haematological profile was unremarkable. He was prepared for an emergency sigmoidoscope. Sigmoidoscopic reduction was successful in resolving the volvulus, but a cause for the obstruction could not be ascertained. He was then investigated for pseudo-obstruction of the colon (Ogilvie’s syndrome) which was negative. The patient was subsequently discharged home with a plan for an elective sigmoid colonic resection. Two weeks later he presented once more with bowel obstruction. His computerised tomography scan showed a sigmoid volvulus with a band at the rectosigmoid junction (Figure 2). The patient consented for an exploratory laparotomy with a possible Hartman’s procedure and intra-operative sigmoidoscope.

(A) CT scan axial view showing the sigmoid volvulus; and (B) coronal view showing the “kidney bean” sign (orange arrow).
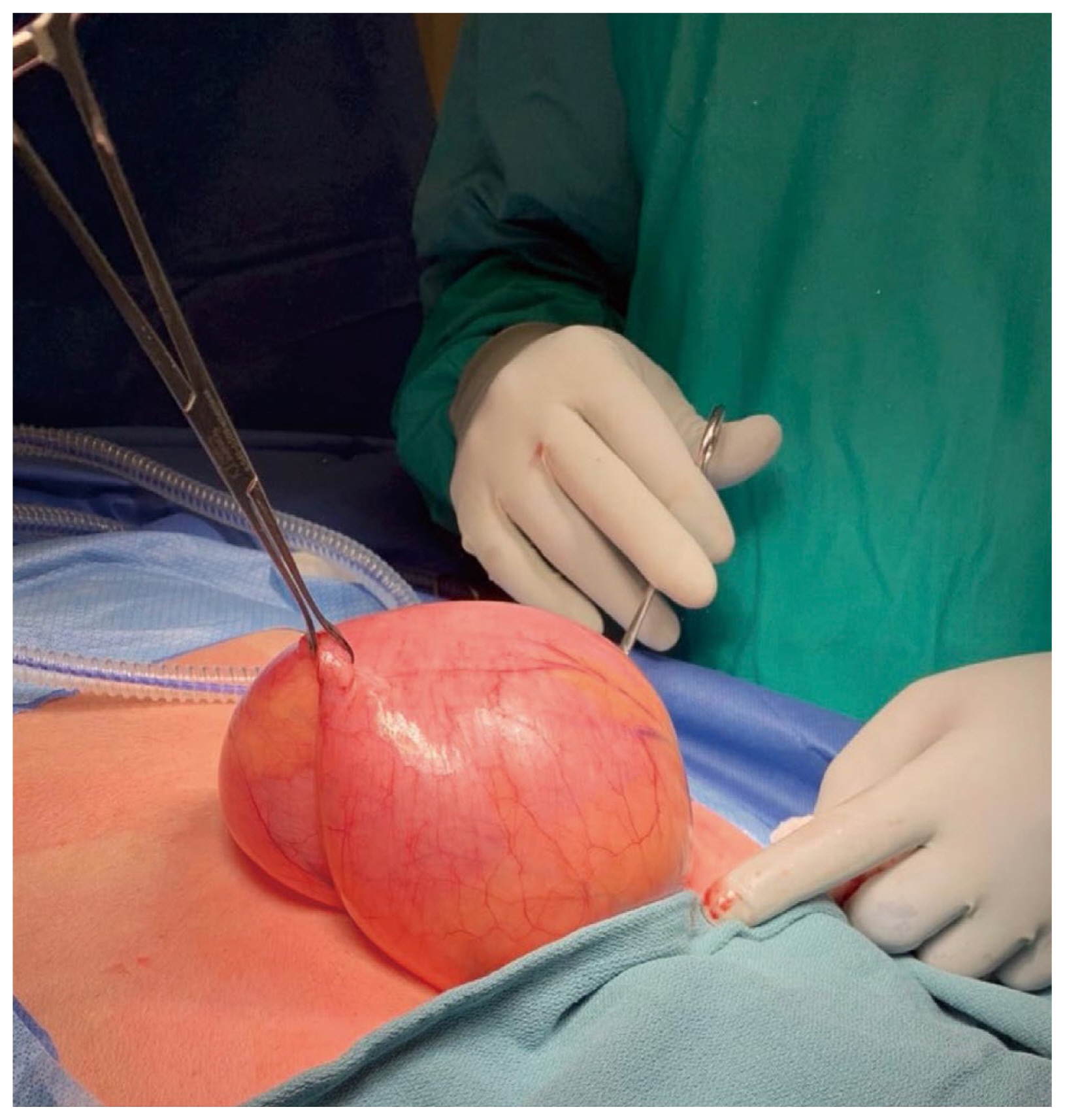
At laparotomy it was observed that the patient had a large sigmoid colon that extended to the right upper quadrant of his abdomen and over his liver (Figures 3, 4A, and 4B). The obstructing band was a congenital defect in the greater omentum (Figures 5A and 5B). This was removed and a partial omentectomy was performed. He also had a sigmoid colectomy and a Hartmann’s colostomy was created. Primary anastomosis was not attempted given the size discrepancy between the left colon and the rectum.
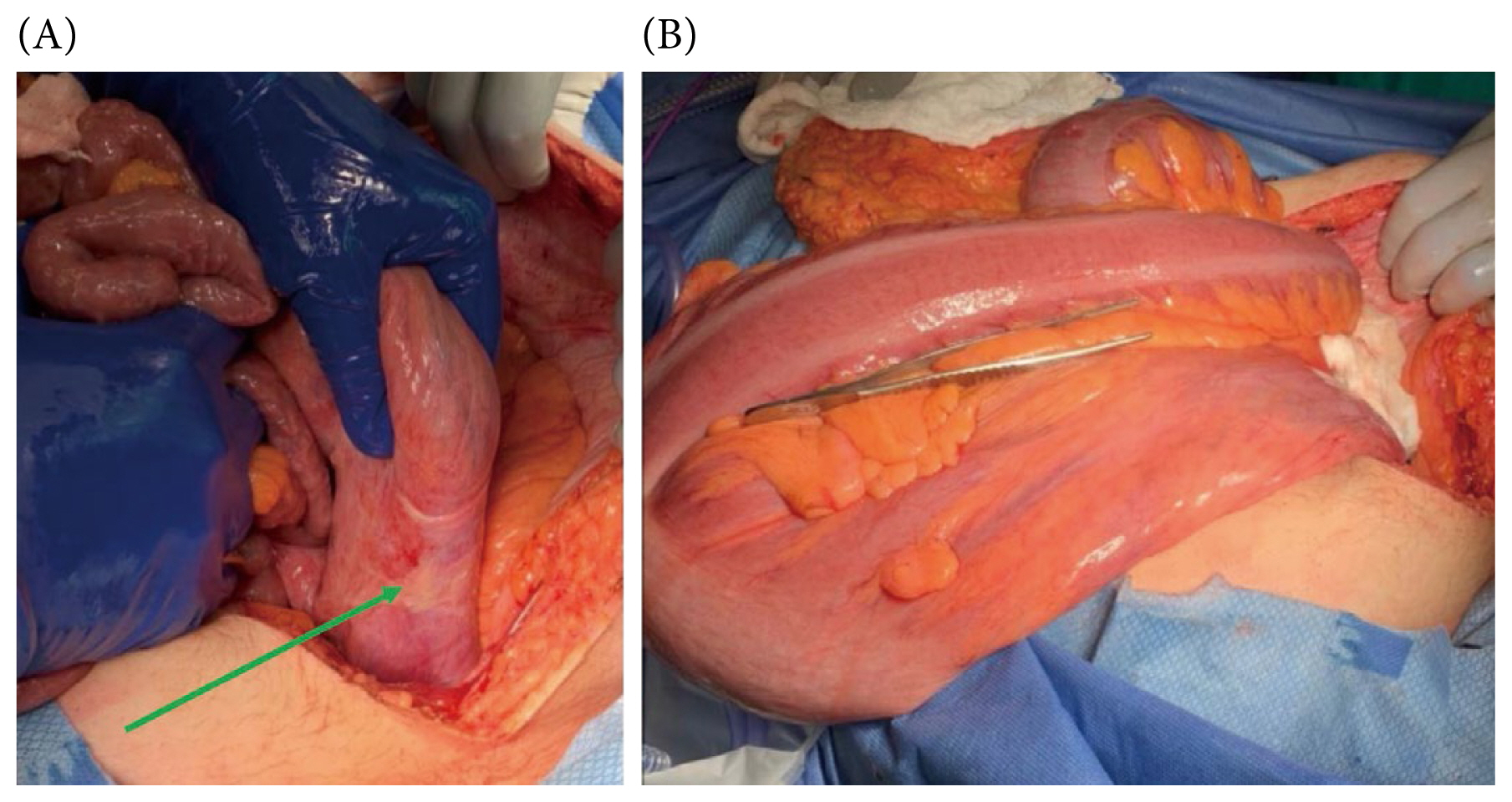
(A) Adhesive band caused by the omental incarceration (green arrow); and (B) large sigmoid colon that extends across the patient’s abdomen post decompression.
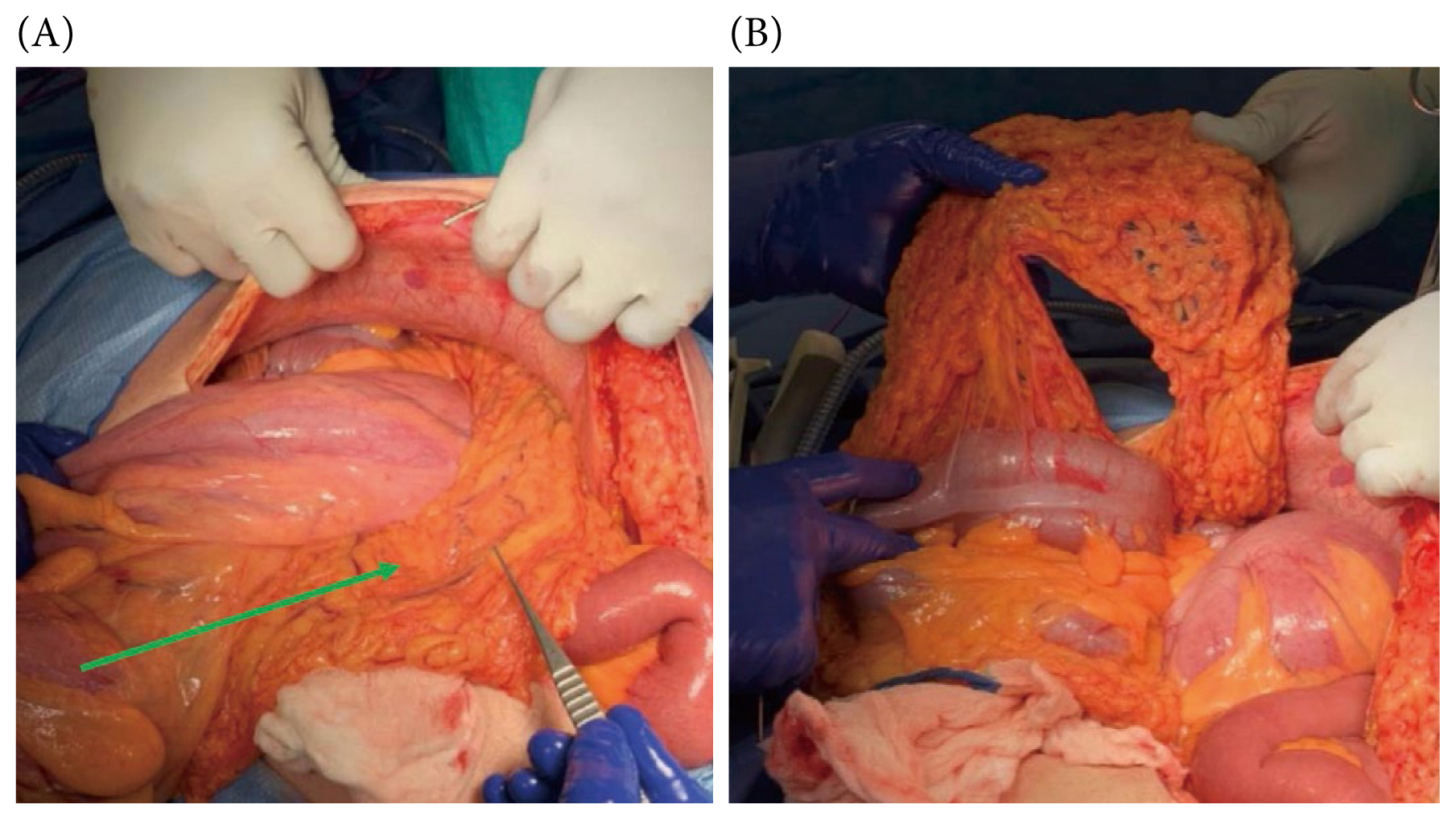
(A) Omentum causing the sigmoid volvulus (green arrow); and (B) the defect in the omentum once the bowel was mobilized.
His recovery was challenging with a midline wound dehiscence and melaena stools passing from his colostomy. The dehiscence was thought to be attributable to his rectus diastasis and thin abdominal wall. He had a relook laparotomy and an intraoperative gastroscopy which revealed a bleeding gastric ulcer. He had secondary suturing to his abdominal wall and the dehiscence was surgically dealt with. The gastric ulcer was injected with adrenaline to affect haemostasis and he was put on H. pylori quadruple eradication therapy. A few days later the melaena stools had stopped being produced. He was able to resume his regular diet, went home after 10 days, and made an eventful recovery. Pathology confirmed regular bowel mucosa and a normal omentum with no surreptitious malignancy. His follow-up plan included a stoma reversal in 18 months.
Discussion
Sigmoid volvulus remains the commonest location of a large bowel volvulus accounting for 70%–80% of cases [3,4]. The pathophysiology involves a mesenteric torsion that creates a closed loop obstruction. In most cases, the aetiology of this condition may be due to a lead point or a mass [5]. This can be intra or extra luminal. Malrotation has been implicated in a caecal volvulus but not in a sigmoid one [6]. To our knowledge this is a unique case report involving a defect in the greater omentum. The omental defect created a circumferential band as an extra luminal lead point resulting in a volvulus. Given the size of the sigmoid colon, as well as the history of the symptoms, this may well have been a congenital omental defect. Congenital trans mesenteric internal hernias, while rare, have been described as a potential source of a sigmoid volvulus [7]. There have been no published case reports to date with a congenital omental defect as a lead point in the pathophysiology of a sigmoid volvulus. This makes for a truly rare aetiology of a rare cause of large bowel obstruction. Irrespective of the aetiology, the management remains the same. Endoscopic detorsion is performed to decompress the colon in the acute phase. This is merely to affect a colonic decompression as the recurrence rate following endoscopy can be between 50%–70% [7]. Acute surgical intervention is undertaken in the presence of bowel ischemia or a failed endoscopic detorsion [8,9]. Surgery can involve a Hartmann’s colostomy or a primary anastomosis. This is the recognised standard of care for a sigmoid volvulus. Laparoscopic intervention has been reported in a few sporadic cases [10]. Surgical pexy of the sigmoid colon without a bowel resection has been attempted [7,10]. These are sporadic accounts with higher recurrence rates, morbidity, and mortality.
Notes
Author Contributions
Concept design, primary surgeon, introduction, abstract and figures: YP. Discussion and references: VN.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Funding
No funding was provided for this article.
Ethical Statement
Informed consent was obtained from the patient.
Data Availability
All relevant data are included in this article.